7 Why Are Lawyers Regulated?
Courts and state legislatures believe that lawyer regulation is needed to “protect the public.”[1] Lawyers possess specialized knowledge that the average client/person does not. A recent Gallup Poll that assesses honesty/ethics in professions put lawyers at “average” when it came to honesty/ethics.
Table 1.1 Response to Gallup poll question: Please tell me how you would rate the honesty and ethical standards of people in these different fields — very high, high, average, low or very low?
|
|
Very high % |
High % |
Average % |
Low % |
Very Low % |
No opinion % |
|
Nurses |
27 |
54 |
16 |
2 |
1 |
— |
|
Medical doctors |
17 |
50 |
25 |
5 |
3 |
* |
|
Grade school teachers |
18 |
46 |
25 |
7 |
4 |
1 |
|
Pharmacists |
17 |
46 |
30 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
|
Military officers |
16 |
45 |
31 |
6 |
2 |
1 |
|
Police officers |
13 |
40 |
32 |
9 |
6 |
* |
|
Day care providers |
10 |
40 |
42 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
|
Judges |
8 |
30 |
43 |
13 |
5 |
* |
|
Clergy |
8 |
28 |
48 |
10 |
4 |
1 |
|
Auto mechanics |
5 |
30 |
51 |
11 |
3 |
* |
|
Nursing home operators |
6 |
21 |
46 |
18 |
9 |
1 |
|
Bankers |
3 |
24 |
52 |
14 |
6 |
* |
|
Local officeholders |
2 |
20 |
54 |
17 |
7 |
1 |
|
Lawyers |
3 |
16 |
50 |
21 |
9 |
1 |
|
Newspaper reporters |
4 |
13 |
39 |
26 |
17 |
* |
|
Business executives |
2 |
13 |
50 |
25 |
9 |
1 |
|
TV reporters |
2 |
12 |
38 |
27 |
21 |
* |
|
State officeholders |
1 |
11 |
48 |
29 |
10 |
* |
|
Advertising practitioners |
1 |
10 |
44 |
31 |
12 |
2 |
|
Members of Congress |
3 |
6 |
29 |
37 |
25 |
1 |
|
Car salespeople |
1 |
7 |
49 |
31 |
11 |
1 |
|
Lobbyists |
1 |
4 |
28 |
35 |
28 |
4 |
Law often represents an ethical minimum. Ethics often represents a standard that exceeds the legal minimum.
Source: https://news.gallup.com/poll/1654/honesty-ethics-professions.aspx
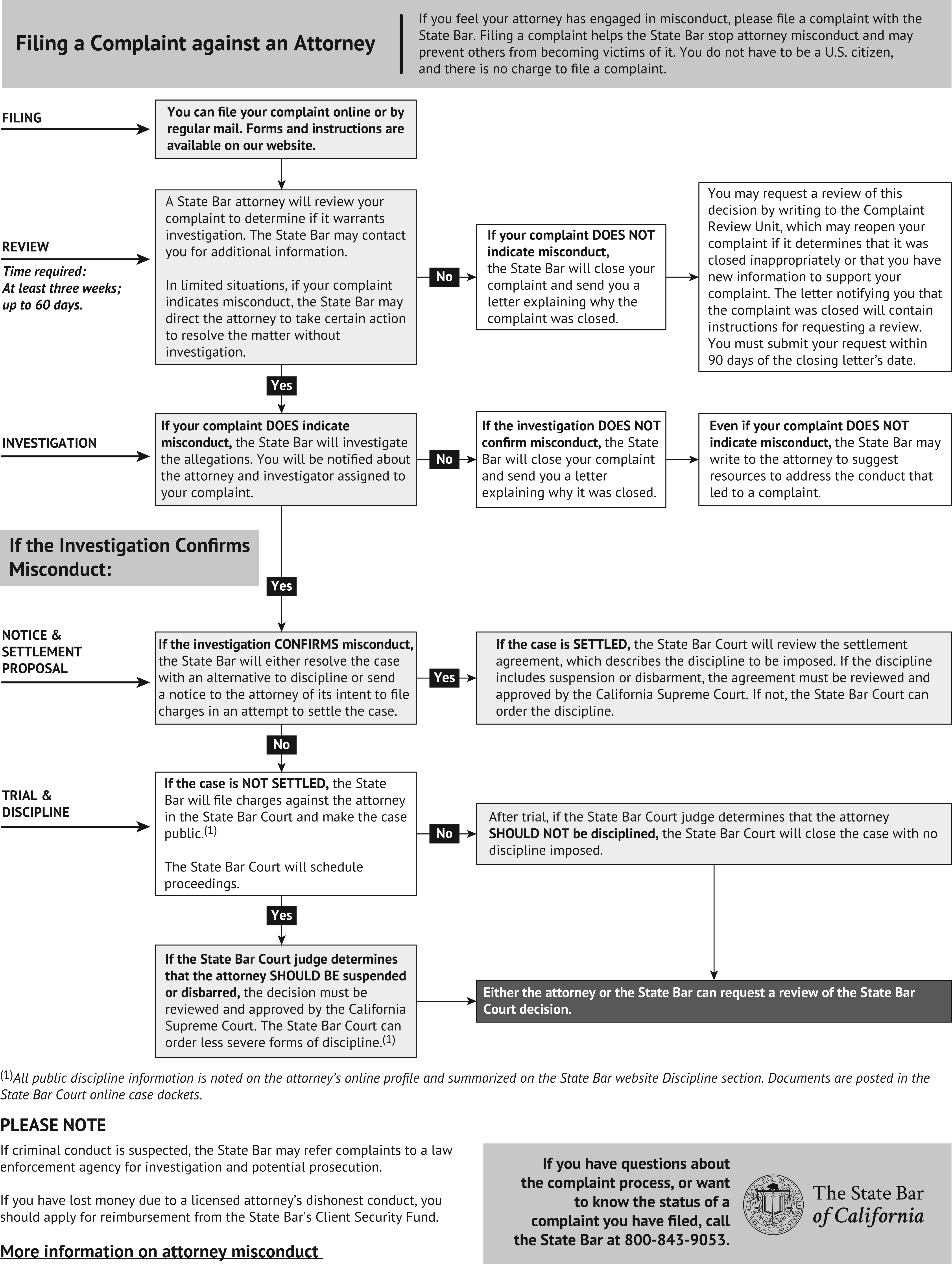
For this reason, state bar associations provide a forum for clients to register complaints against lawyers. These complaints usually pertain to situations where the attorney has acted unethically. However, often complaints are initiated because clients are unhappy with the outcome in a case or have a problem with their billing or attorney fees. Interestingly, many states do not have a statute of limitation on complaints. However, once a complaint is filed, a state bar has a set time frame within which it must start disciplinary proceedings against an attorney.
In many states, besides filing a complaint, the public can search the state bar’s website to check whether an attorney has a public record of prior discipline. Additionally, in instances where there is a fee dispute, a client may resolve such dispute “through an informal, confidential, and low-cost alternative called Mandatory Fee Arbitration.”[2] See the Additional Resources section at the end of the chapter for a sample complaint form and a “Look Up a Lawyer” example.
- Fred C. Zacharias, “The Purpose of Lawyer Discipline,” William & Mary Law Review 45, no. 2 (December 2003): 675–745, https://scholarship.law.wm.edu/wmlr/vol45/iss2/6. ↵
- “Resolving Fee Disputes with Your Attorney,” The State Bar of California, n.d., http://www.calbar.ca.gov/Public/Free-Legal-Information/Resolving-Problems/Lawyer-Fee-Dispute. ↵